The Enigma of Syncope: Exploring the Frequency of Fainting
Related Articles: The Enigma of Syncope: Exploring the Frequency of Fainting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Enigma of Syncope: Exploring the Frequency of Fainting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigma of Syncope: Exploring the Frequency of Fainting

Fainting, medically termed syncope, is a common experience that affects individuals across all ages and demographics. While generally benign and self-limiting, understanding its prevalence and underlying causes is crucial for addressing potential underlying medical conditions and ensuring prompt and appropriate medical attention when necessary.
Defining Fainting: A Complex Phenomenon
Fainting is characterized by a temporary loss of consciousness due to a sudden reduction in blood flow to the brain. This reduction can stem from various factors, including:
- Vasovagal Syncope: The most common type, triggered by emotional distress, pain, or prolonged standing. It involves a sudden decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, leading to a reduced blood supply to the brain.
- Cardiac Syncope: Caused by heart rhythm abnormalities, such as bradycardia (slow heart rate) or tachycardia (fast heart rate), or structural heart problems that impair blood flow.
- Orthostatic Hypotension: Occurs when blood pressure drops significantly upon standing, leading to insufficient blood supply to the brain.
- Neurological Syncope: Can be caused by seizures, migraines, or other neurological conditions that disrupt the brain’s normal function.
Prevalence: A Global Perspective
Accurately determining the frequency of fainting across the globe presents a challenge due to variations in reporting and diagnostic practices. However, studies suggest that syncope is a relatively common occurrence, with estimates indicating that:
- Approximately 15-35% of individuals will experience at least one fainting episode in their lifetime. This wide range reflects the diverse causes and triggers of fainting.
- The incidence of syncope increases with age, particularly after 65 years. This is likely due to age-related changes in cardiovascular function and increased susceptibility to underlying medical conditions.
- Women are more likely to experience fainting than men. This may be attributed to hormonal fluctuations, particularly during menstruation and pregnancy.
Factors Influencing Fainting Frequency
Several factors can influence the frequency of fainting episodes, including:
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of fainting.
- Medications: Some medications, particularly those affecting blood pressure or heart rate, can contribute to fainting episodes.
- Lifestyle Factors: Dehydration, excessive caffeine intake, and lack of sleep can all increase susceptibility to fainting.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme heat, humidity, and standing for prolonged periods can trigger fainting.
The Significance of Fainting: Beyond a Transient Event
While most fainting episodes are harmless and resolve spontaneously, understanding their frequency and potential causes is crucial for several reasons:
- Identifying Underlying Medical Conditions: Fainting can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions that require treatment.
- Preventing Future Episodes: Identifying triggers and addressing risk factors can help reduce the frequency of fainting.
- Ensuring Safety: Fainting can lead to falls and injuries, particularly in elderly individuals.
- Managing Medical Conditions: Fainting can be a sign of worsening health conditions that require medical attention.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
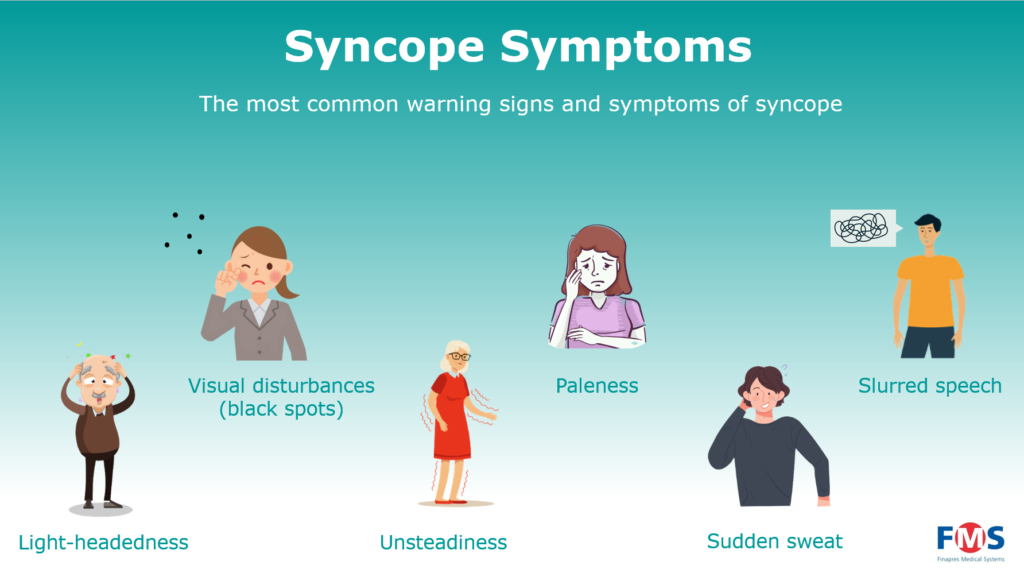
Q: What are the most common symptoms of fainting?
A: The most common symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, blurred vision, sweating, and a feeling of weakness or fatigue. Some individuals may experience a brief loss of consciousness or a feeling of detachment from their surroundings.
Q: How long does a fainting episode typically last?
A: Fainting episodes usually last only a few seconds to a few minutes. However, some individuals may experience prolonged episodes that last for several minutes or even hours.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for fainting?
A: You should seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Frequent fainting episodes
- Fainting accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or seizures
- Fainting that occurs without any apparent trigger
- Fainting that lasts longer than a few minutes
Q: What are some tips to prevent fainting?
A: Here are some tips to help prevent fainting:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Avoid standing for long periods: Take breaks to sit or lie down.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol: These substances can dehydrate you and lower blood pressure.
- Eat regular meals: Avoid skipping meals, especially breakfast.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation.
- Get regular exercise: Exercise can improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of fainting.
- Monitor your medications: Discuss any concerns about your medications with your doctor.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Approach to Syncope
Fainting, while often a transient and benign experience, can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions or a sign of worsening health. Understanding the frequency and potential causes of fainting is essential for ensuring prompt medical attention when necessary and implementing preventive measures to reduce the risk of future episodes. By recognizing the diverse factors that can contribute to syncope and seeking appropriate medical evaluation, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and minimize the potential consequences of this common yet sometimes perplexing phenomenon.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigma of Syncope: Exploring the Frequency of Fainting. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
