A Tapestry of Trends: The Evolution of Fashion Through the Ages
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Trends: The Evolution of Fashion Through the Ages
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Trends: The Evolution of Fashion Through the Ages. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Trends: The Evolution of Fashion Through the Ages

Fashion, a constantly evolving reflection of society, has been a driving force in human history, shaping not only how we dress but also our perceptions of ourselves and others. Its origins are deeply intertwined with the development of civilization, tracing a fascinating trajectory from practical necessity to a powerful form of self-expression.
The Dawn of Fashion: Practicality and Identity
The earliest forms of "fashion" were driven by necessity. In prehistoric times, clothing served as protection from the elements, made from readily available materials like animal skins and woven plant fibers. This period witnessed the emergence of distinct clothing styles based on geographic location, climate, and available resources. For example, the elaborate headdresses and intricate body paint of indigenous tribes in Africa and the Americas served as both practical adornment and symbolic representations of tribal identity.
The rise of agriculture and the establishment of settled societies brought about significant changes in clothing. The development of weaving and dyeing techniques allowed for the creation of more sophisticated garments, often reflecting social status and occupation. In ancient Egypt, linen garments became a staple, while the elaborate costumes of priests and pharaohs showcased their power and authority.
The Classical World: Elegance and Status
The ancient civilizations of Greece and Rome further refined the concept of fashion. The Greeks emphasized simplicity and elegance, favoring flowing tunics and robes made from fine fabrics like wool and linen. Roman clothing, while influenced by Greek styles, incorporated more elaborate designs and ornamentation, reflecting the growing influence of social hierarchy.
The toga, a draped garment worn by both men and women, became a symbol of Roman citizenship. The color and style of the toga indicated the wearer’s social status, with senators wearing purple and ordinary citizens opting for plain white. This emphasis on status through clothing laid the foundation for the later evolution of fashion as a means of social differentiation.
The Middle Ages: Religious Influence and Regional Diversity
The Middle Ages saw a shift in fashion trends, influenced by the rise of Christianity and the dominance of regional styles. Clothing became more modest, with women covering their hair and bodies. The influence of the Church was evident in the widespread adoption of the tunic, a long, loose-fitting garment, and the cloak, a symbol of piety and protection.
The period also saw the emergence of distinct regional styles. The French were known for their elegant and refined attire, while the Italians developed a taste for elaborate fabrics and ornamentation. The rise of the merchant class in northern Europe led to the introduction of new fabrics and fashion trends, further diversifying the fashion landscape.
The Renaissance: A Rebirth of Fashion
The Renaissance marked a turning point in fashion history. The rediscovery of classical art and literature led to a renewed interest in beauty and elegance. Clothing became more elaborate and ornate, with a focus on symmetry, proportion, and the human form.
The rise of the Italian city-states, centers of art and commerce, fueled the development of new fashion trends. The introduction of new fabrics like silk and velvet from the East brought about a wave of luxury and sophistication. Men’s fashion became increasingly flamboyant, with elaborate breeches, doublets, and hose. Women’s clothing, while still modest, emphasized the curves of the body with tight-fitting bodices and voluminous skirts.
The Baroque Era: Opulence and Excess
The Baroque era, characterized by its dramatic and theatrical style, further elevated fashion to new heights of extravagance. Clothing became even more elaborate, with an emphasis on rich fabrics, elaborate embroidery, and lavish ornamentation.
The French court under King Louis XIV set the standard for fashion, with its opulent gowns, powdered wigs, and high heels. The influence of the French court spread throughout Europe, solidifying the role of fashion as a symbol of power and status.
The 18th Century: Enlightenment and Elegance
The 18th century witnessed a shift towards a more refined and elegant style. The Enlightenment emphasized reason and rationality, influencing fashion to become more practical and less extravagant.
The Rococo period, with its emphasis on lightness and grace, saw the introduction of new fabrics like muslin and cotton. Women’s dresses became more streamlined and feminine, with emphasis on delicate details and pastel colors. Men’s fashion also became more streamlined, with the introduction of the three-piece suit.
The 19th Century: Romanticism and Industrialization
The 19th century was a period of dramatic change, marked by the rise of romanticism and the Industrial Revolution. Fashion reflected these changes, embracing both the romantic ideal of the past and the innovations of the present.
Romanticism influenced fashion with its emphasis on nature and emotion. Women’s dresses became more flowing and ethereal, with a focus on natural fabrics and delicate details. The rise of the crinoline, a cage-like structure worn beneath the skirt, created a dramatic silhouette that emphasized the feminine form.
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in fashion production. The invention of the sewing machine and the development of new fabrics like synthetic dyes made clothing more affordable and accessible to a wider range of people. This period also saw the rise of fashion magazines and department stores, further democratizing fashion and making it a more global phenomenon.
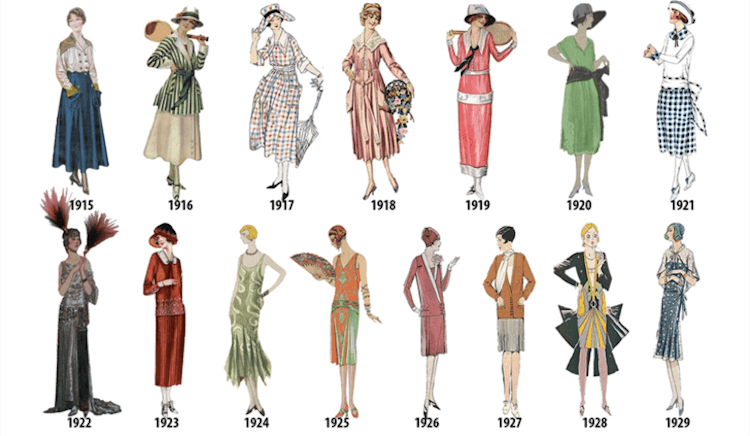
The 20th Century: Modernism, Rebellion, and Mass Production
The 20th century saw a rapid evolution of fashion, reflecting the social and cultural changes of the time. Modernism, with its emphasis on simplicity and functionality, influenced fashion to become more streamlined and practical. The rise of the flapper in the 1920s brought about a shift towards shorter skirts, looser dresses, and a more androgynous style.
The 1930s and 1940s were marked by the influence of the Great Depression and World War II. Fashion became more austere and utilitarian, with a focus on practicality and durability. The post-war era saw a return to glamour and femininity, with the introduction of the "New Look" by Christian Dior, characterized by its full skirts and cinched waists.
The 1960s and 1970s witnessed a cultural revolution, with fashion reflecting the spirit of rebellion and counterculture. The rise of youth culture, the civil rights movement, and the women’s liberation movement all had a profound impact on fashion. The introduction of new fabrics like stretch fabrics and synthetic fibers allowed for more comfortable and versatile clothing.
The latter half of the 20th century saw the rise of mass production, with fast fashion becoming increasingly prevalent. This trend, while making clothing more affordable and accessible, also led to concerns about environmental sustainability and the exploitation of labor.
The 21st Century: Globalization and Digital Influence
The 21st century has witnessed a further globalization of fashion, with trends originating from all over the world. The rise of social media and e-commerce has further democratized fashion, allowing individuals to express themselves through clothing and access trends from around the globe.
The influence of pop culture and celebrity culture has also played a significant role in shaping contemporary fashion trends. Fashion has become more fluid and experimental, with a focus on individuality and self-expression.
FAQs
What are the driving forces behind fashion trends?
Fashion trends are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Social and Cultural Factors: Social and cultural changes, such as technological advancements, political events, and social movements, often influence fashion trends.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions, such as the availability of resources and the purchasing power of consumers, can impact fashion trends.
- Technological Factors: Technological advancements, such as new fabrics, manufacturing techniques, and communication technologies, can shape fashion trends.
- Artistic and Creative Influences: Art, music, and other forms of creative expression often inspire fashion trends.
- Media and Marketing: The media, including fashion magazines, television, and social media, plays a significant role in shaping and promoting fashion trends.
How do fashion trends spread?
Fashion trends spread through a variety of channels, including:
- Word of Mouth: People often learn about new trends through conversations with friends and family.
- Media: Fashion magazines, television shows, and social media platforms all play a role in spreading fashion trends.
- Celebrities: Celebrities often set fashion trends by wearing specific items or styles.
- Fashion Shows: Fashion shows are major events that showcase new trends and designs.
- Retailers: Retailers play a role in spreading fashion trends by stocking and promoting specific items.
What is the importance of fashion trends?
Fashion trends are important for a number of reasons:
- Self-Expression: Fashion allows individuals to express their personality, style, and beliefs through clothing.
- Social Identity: Fashion can help people to identify with specific groups or communities.
- Economic Impact: Fashion is a major industry that contributes significantly to the global economy.
- Cultural Exchange: Fashion can facilitate cultural exchange and understanding.
Tips for Understanding Fashion Trends:
- Stay Informed: Keep up with current fashion trends by reading fashion magazines, watching fashion shows, and following fashion bloggers.
- Experiment: Don’t be afraid to try new styles and experiment with different looks.
- Find Your Personal Style: Develop your own unique sense of style that reflects your personality and preferences.
- Consider the Context: Think about the occasion, the setting, and your personal style when choosing what to wear.
- Invest in Quality: Choose well-made clothing that will last longer and look better over time.
Conclusion
The history of fashion trends is a fascinating journey through time, reflecting the evolution of society, culture, and technology. From the practical needs of our ancestors to the elaborate styles of the Renaissance and the rebellious trends of the 20th century, fashion has always been a powerful force, shaping our perceptions of ourselves and others. As we move forward into the future, it remains to be seen what new trends will emerge and how they will reflect the changing world around us. The one constant, however, is the enduring power of fashion as a form of self-expression, social identity, and cultural exchange.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Trends: The Evolution of Fashion Through the Ages. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
